Contributors and funding
Overview of departments and funding sources contributing to DAIC.
less than a minute
A high-performance computing (HPC) cluster is a collection of interconnected compute resources (like CPUs, GPUs, memory, and storage) shared among a group of users. These resources work together to perform lengthy and computationally intensive tasks that would be too large or too slow on a single computer. HPC is especially useful for modern scientific computing applications, where datasets are typically large, models are complex, and computations require specialized hardware (such as GPUs or FPGAs).
The Delft AI Cluster (DAIC), formerly known as INSY-HPC (or simply “HPC”), is a TU Delft high-performance computing cluster consisting of Linux compute nodes (i.e., servers) with substantial processing power and memory for running large, long, or GPU-enabled jobs.
What started in 2015 as a CS-only cluster has grown to serve researchers across many TU Delft departments. Each expansion has continued to support the needs of computer science and AI research. Today, DAIC nodes are organized into partitions that correspond to the groups contributing those resources. (See Contributing departments and TU Delft clusters comparison.)
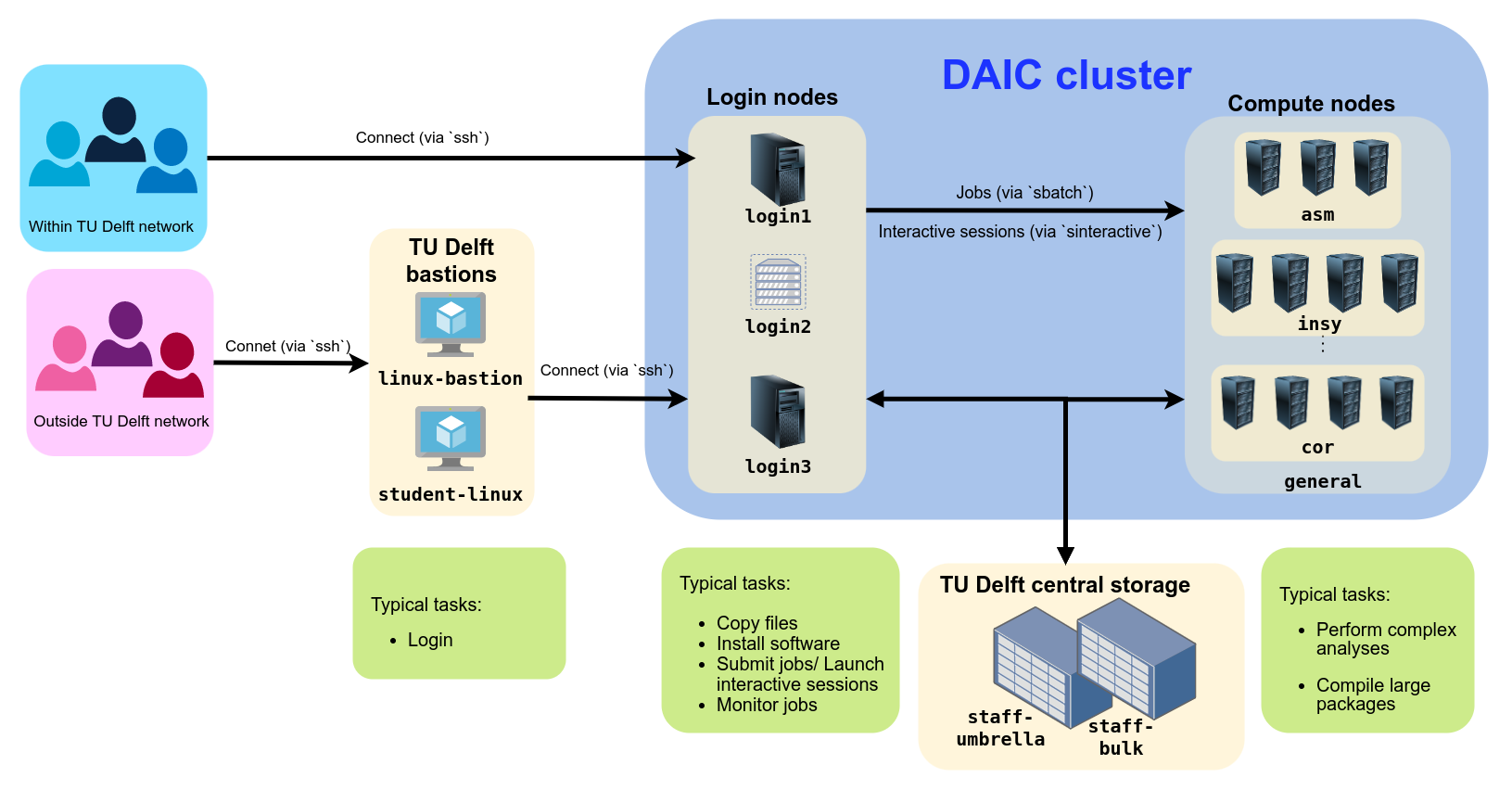
DAIC partitions and access/usage best practices
Overview of departments and funding sources contributing to DAIC.
Meet the DAIC advisory board and learn how to cite, acknowledge, and measure the scientific impact of DAIC.