This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Tutorials
1 - Customize your shell
Source .bashrc upon login
.bashrc is a configuration file for the Bash shell, which is the default command-line shell on many Linux and Unix-based systems. It is a hidden file located in the user’s home directory (~/.bashrc) and is executed every time a new interactive Bash session starts. The file contains settings that customize the shell’s behavior, such as defining environment variables, setting prompt appearance, and specifying terminal options.
Edit or create the file ~/.profile and insert the following line:
source ~/.bashrc
Now, your .bashrc will be loaded upon login.
Customize prompt and aliases.
Aliases are custom shortcuts or abbreviations for longer commands in the shell. They allow you to define a shorter, user-friendly command that, when executed, will perform a longer or more complex command. For example, you might create an alias like alias ll='ls -la' in your .bashrc file to quickly list all files in a directory in long format. Aliases can help improve productivity by saving time and effort when working with the shell. You can set these configurations permanently by editing your ~/.bashrc file.
## Add these lines to your ~/.bashrc file to make use of these settings.
# Alias
alias ll='ls -alF'
alias la='ls -A'
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
alias l='ls -rtlh --full-time --color=auto'
alias md='mkdir'
alias ..='cd ..'
alias ...='cd ../..'
alias ....='cd ../../..'
alias src='source ~/.bashrc'
## Slurm helpers
alias interactive='srun --pty --nodes=1 --ntasks=1 --cpus-per-task=4 --mem=8G --time=1:00:00 bash'
alias st='sacct --format=JobID,JobName%30,State,Elapsed,Timelimit,AllocNodes,Priority,Start,NodeList'
alias sq="squeue -u $USER --format='%.18i %.12P %.30j %.15u %.2t %.12M %.6D %R'"
alias slurm-show-my-accounts='sacctmgr list user "$USER" withassoc format="user%-20,account%-45,maxjobs,maxsubmit,maxwall,maxtresperjob%-40"'
alias slurm-show-all-accounts='sacctmgr show account format=Account%30,Organization%30,Description%60'
alias slurm-show-nodes='sinfo -lNe'
# Shellstyle
## Assuming your shell background is black!
## Prompt setting (readable prompt colors and username@hostname:)
export PS1='\[\033[01;96m\]\u\[\033[0m\]@\[\033[01;32m\]\h\[\033[0m\]:\[\033[96m\]\w\[\033[00m\]\$ '
## ls colors (readable ls colors)
export LS_COLORS='rs=0:di=1;35:ln=01;36:mh=00:pi=40;33:so=01;35:do=01;35:bd=40;33;01:cd=40;33;01:or=40;31;01:su=37;41:sg=30;43:ca=30;41:tw=30;42:ow=34;42:st=37;44:ex=01;32:*.tar=01;31:*.tgz=01;31:*.arj=01;31:*.taz=01;31:*.lzh=01;31:*.lzma=01;31:*.tlz=01;31:*.txz=01;31:*.zip=01;31:*.z=01;31:*.Z=01;31:*.dz=01;31:*.gz=01;31:*.lz=01;31:*.xz=01;31:*.bz2=01;31:*.bz=01;31:*.tbz=01;31:*.tbz2=01;31:*.tz=01;31:*.deb=01;31:*.rpm=01;31:*.jar=01;31:*.war=01;31:*.ear=01;31:*.sar=01;31:*.rar=01;31:*.ace=01;31:*.zoo=01;31:*.cpio=01;31:*.7z=01;31:*.rz=01;31:*.jpg=01;35:*.jpeg=01;35:*.gif=01;35:*.bmp=01;35:*.pbm=01;35:*.pgm=01;35:*.ppm=01;35:*.tga=01;35:*.xbm=01;35:*.xpm=01;35:*.tif=01;35:*.tiff=01;35:*.png=01;35:*.svg=01;35:*.svgz=01;35:*.mng=01;35:*.pcx=01;35:*.mov=01;35:*.mpg=01;35:*.mpeg=01;35:*.m2v=01;35:*.mkv=01;35:*.webm=01;35:*.ogm=01;35:*.mp4=01;35:*.m4v=01;35:*.mp4v=01;35:*.vob=01;35:*.qt=01;35:*.nuv=01;35:*.wmv=01;35:*.asf=01;35:*.rm=01;35:*.rmvb=01;35:*.flc=01;35:*.avi=01;35:*.fli=01;35:*.flv=01;35:*.gl=01;35:*.dl=01;35:*.xcf=01;35:*.xwd=01;35:*.yuv=01;35:*.cgm=01;35:*.emf=01;35:*.axv=01;35:*.anx=01;35:*.ogv=01;35:*.ogx=01;35:*.aac=00;36:*.au=00;36:*.flac=00;36:*.mid=00;36:*.midi=00;36:*.mka=00;36:*.mp3=00;36:*.mpc=00;36:*.ogg=00;36:*.ra=00;36:*.wav=00;36:*.axa=00;36:*.oga=00;36:*.spx=00;36:*.xspf=00;36:';
REIT bash configuration
An example configuration is available here: https://gitlab.ewi.tudelft.nl/reit/shell-config
2 - Apptainer tutorial
What and Why containerization?
Containerization packages your software, libraries, and dependencies into a single portable unit: a container. This makes your application behave the same way everywhere: on your laptop, in the cloud, or on DAIC. This means:
- Consistency: The application runs the same way regardless of where it’s executed. You can develop on one machine, test on another, and deploy on a cluster without worrying about dependency differences.
- Isolation: Each container is independent from others, preventing conflicts and enhancing security and reliability.
- Portability: Containers can run on different systems without modification, simplifying movement between servers, clusters, or clouds.
- Efficiency: Containers share the host system’s resources like the operating system, making them lightweight and fast to start compared to virtual machines.
On DAIC specifically, users often encounter issues with limited home directory space or Windows-based /tudelft.net mounts (see Storage), which can complicate the use of conda/mamba and/or pip. Containers offer a solution by encapsulating all software and dependencies in a self-contained environment. You can, for instance, store containers on staff-umbrella with all required dependencies, including those installed via pip, and run them reliably and reproducibly without being limited by home directory size or mount compatibility.
Containerization on DAIC: Apptainer
DAIC supports Apptainer (previously Apptainer), an open-source container platform, designed to run on High-performance computing environments. Apptainer runs container images securely on shared clusters and allows you to use Docker images directly, without needing Docker itself.
A typical Apptainer workflow revolves around three key components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
Definition file (*.def) | A recipe describing how to build the container: which base image to use and which packages to install. |
Image (*.sif) | A single portable file containing the full environment: operating system, libraries, and applications. |
| Container | A running instance of an image, with its own writable workspace for temporary files or intermediate data. |
Because Apptainer integrates well with Slurm, containers can be launched directly within batch jobs or interactive sessions on DAIC.
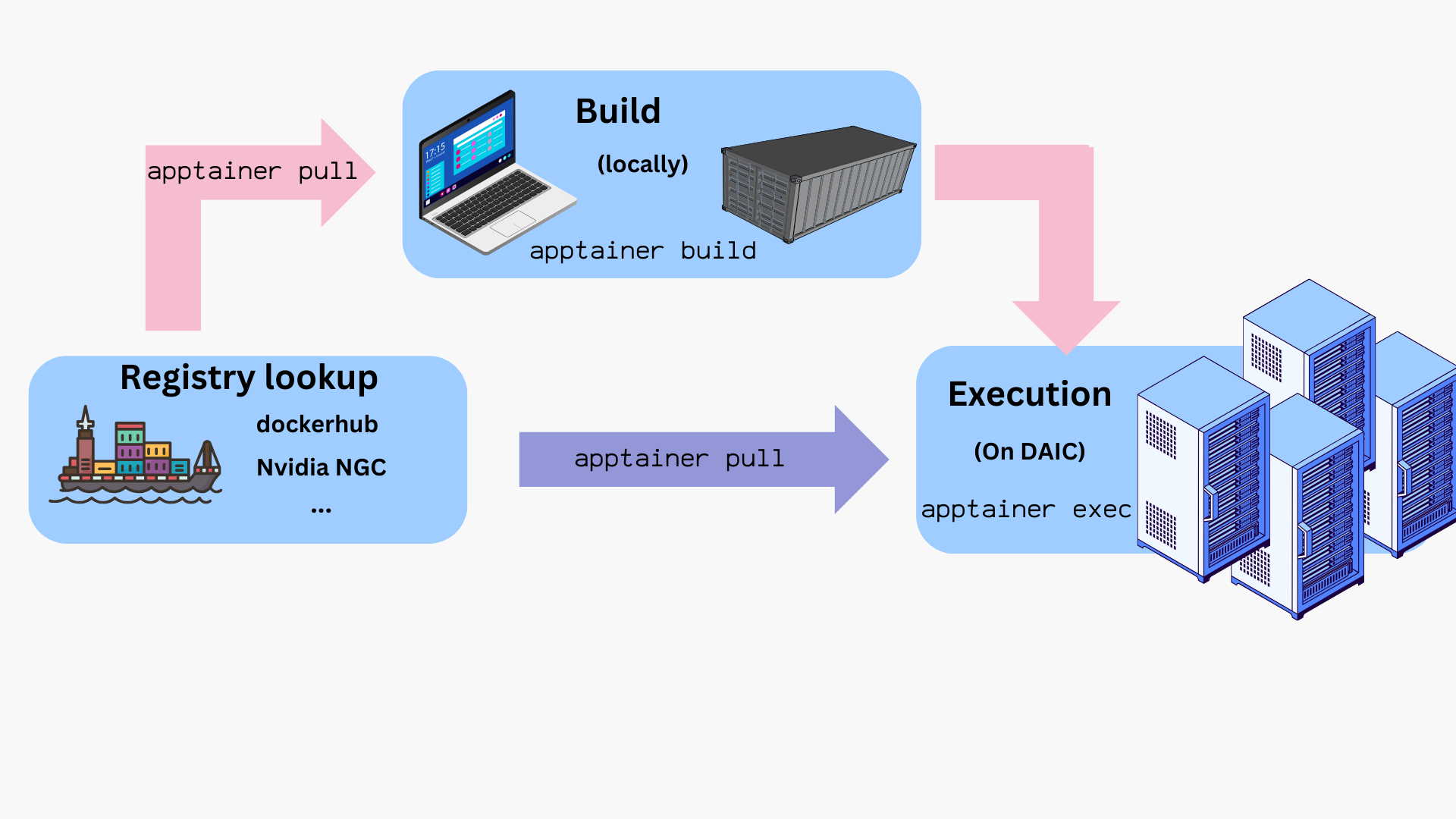
The following sections show how to obtain, build, and run images.
Workflow overview
The typical lifecycle for containers on DAIC is:
- Build the image locally from a
.deffile. - Transfer or pull the resulting
.siffile onto DAIC. - Test interactively using
sinteractiveon a compute node. - Run in a batch job with
sbatchorsrunusingapptainer execorapptainer run. - Provision bind mounts, GPU flags, and cache locations as needed.
- Clean up and manage storage (e.g.,
APPTAINER_CACHEDIR).
How to run commands/programs inside a container?
Once you have a container image (e.g., myimage.sif), you can launch it in different ways depending on how you want to interact with it:
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
apptainer shell <image> | Start an interactive shell inside the container. | apptainer shell myimage.sif |
apptainer exec <image> <command> | Run the <command> inside the container, then exit. | apptainer exec myimage.sif python --version |
apptainer run <image> | Execute the container’s default entrypoint (defined in its recipe). | apptainer run myimage.sif |
where:
<image>is the path to a container image, typically, a*.siffile.
Tips:
- Use
shellfor exploration or debugging inside the container. - Use
execorrunfor automation, workflows, or Slurm batch jobs. - Add
-Cor-cto isolate the container filesystem (see Exposing host directories).
Tip: Test interactively before submitting jobs
For containers that need GPUs or large memory, start an interactive session first:
$ hostname # To check this is DAIC. login[1-3] are the login nodes
login1.daic.tudelft.nl
$ sinteractive --gres=gpu:1 --mem=8G --time=01:00:00 # Request an interactive session with 1 GPU, 8GB memory, 1 hour time
Note: interactive sessions are automatically terminated when they reach their time limit (1 hour)!
srun: job 8543393 queued and waiting for resources
srun: job 8543393 has been allocated resources
13:35:30 up 5 days, 3:41, 0 users, load average: 8,79, 7,60, 7,11
$ hostname # To check we are on a compute node
grs3.daic.tudelft.nl
$ apptainer exec --nv myimage.sif python script.py
This helps verify everything works before submitting a batch job with sbatch or srun.
How to get container files?
You can obtain container images in two main ways:
- Pull prebuilt images by pulling from a container registry/repository (see Using prebuilt images).
- Build your own image locally using a definition file (
*.def), then transfer the resulting.siffile to DAIC (see Building images).
1. Using prebuilt images
Apptainer allows pulling and using images directly from repositories like DockerHub, BioContainers, NVIDIA GPU Cloud (NGC), and others.
Example: Pulling from DockerHub
$ hostname # check this is DAIC
login1.daic.tudelft.nl
$ mkdir ~/containers && cd ~/containers # as convenience, use this directory
$ apptainer pull docker://ubuntu:latest # actually pull the image
INFO: Converting OCI blobs to SIF format
INFO: Starting build...
Getting image source signatures
Copying blob 837dd4791cdc done
Copying config 1f6ddc1b25 done
Writing manifest to image destination
Storing signatures
...
INFO: Creating SIF file...
Now, to check the obtained image file:
$ ls
ubuntu_latest.sif
$ apptainer exec ubuntu_latest.sif cat /etc/os-release # execute cat command and exit
PRETTY_NAME="Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS"
NAME="Ubuntu"
VERSION_ID="22.04"
VERSION="22.04.2 LTS (Jammy Jellyfish)"
VERSION_CODENAME=jammy
ID=ubuntu
ID_LIKE=debian
HOME_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/"
SUPPORT_URL="https://help.ubuntu.com/"
BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/"
PRIVACY_POLICY_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/legal/terms-and-policies/privacy-policy"
UBUNTU_CODENAME=jammy
$ ls /.apptainer.d/ # container-specific directory should not be found on host
ls: cannot access /.apptainer.d/: No such file or directory
$ apptainer shell ubuntu_latest.sif # launch container interactively
Apptainer>
Apptainer> hostname
login1.daic.tudelft.nl
Apptainer> ls
ubuntu_latest.sif
Apptainer> ls /.apptainer.d/
Apptainer actions env labels.json libs runscript startscript
Apptainer> exit
Notes:
- Inside the container, the command prompt changes to
Apptainer> - The container inherits your environment (e.g.,
$HOME,hostname) but has its own internal filesystem (e.g./.apptainer.d)
Tip: Isolate your host filesystem
To prevent accidental deletes/edits, add a -c or -C flags to your apptainer commands to isolate filesystems. For example:
$ apptainer shell -C ubuntu_latest.sif
Example: Pulling from NVIDIA GPU cloud (NGC)
NGC provides pre-built images for GPU accelerated applications. These images are large, and one is recommended to download them locally (in your machine), and then transfer to DAIC. To install Apptainer in your machine, follow the official Installing Apptainer instructions.
Important: Cache and filesystem limits
By default, Apptainer images are saved to ~/.apptainer. To avoid quota issues, set the environment variable APPTAINER_CACHEDIR to a different location.
export APPTAINER_CACHEDIR=/tudelft.net/staff-umbrella/<YourDirectory>/apptainer/cache
Pulling directly to bulk or umbrella is not supported, so pull large images locally, then copy the *.sif file to DAIC.
$ hostname #check this is your own PC/laptop
$ apptainer pull docker://nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:23.05-py3
$ scp pytorch_23.05-py3.sif hpc-login:/tudelft.net/staff-umbrella/...<YourDirectory>/apptainer
Test the image on DAIC:
$ hostname # check this is DAIC not your own PC/laptop
login1.daic.tudelft.nl
$ cd /tudelft.net/staff-umbrella/...<YourDirectory>/apptainer # path where you put images
$ sinteractive --gres=gpu:1 --time=00:05:00 # request a gpu node
$ apptainer shell -C --nv pytorch_23.05-py3.sif #--nv to use NVIDIA GPU and have CUDA support
Apptainer> python -c "import torch; print(torch.cuda.is_available())"
True
2. Building images
If you prefer (or need) a custom container image, you can build one from a definition file (*.def), that specifies your dependencies and setup steps.
On DAIC, you can build images directly if your current directory allows writes and sufficient quota (e.g., under staff-umbrella).
For large or complex builds, it can be more convenient to build locally on your workstation and then transfer the resulting .sif file to DAIC.
Tip: Root privileges not always required
Apptainer supports rootless builds.
You only need sudo when:
- building from base images that require root setup (e.g.,
Bootstrap: dockeron older systems), or - writing the resulting image to a protected location.
Otherwise, you can directly build using:
$ apptainer build myimage.sif myimage.def
Example: CUDA-enabled container
An example definion file, cuda_based.def, for a cuda-enabled container may look as follows:
# Header
Bootstrap: docker
From: nvidia/cuda:12.1.1-devel-ubuntu22.04
# (Optional) Sections/ data blobs
%post
apt-get update # update system
apt-get install -y git # install git
git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/cuda-samples.git # clone target repository
cd cuda-samples
git fetch origin --tags && git checkout v12.1 # fetch certain repository version
cd Samples/1_Utilities/deviceQuery && make # install certain tool
%runscript
/cuda-samples/Samples/1_Utilities/deviceQuery/deviceQuery
where:
- The header, specifies the source (eg,
Bootstrap: docker) and the base image (From: nvidia/cuda:12.1.1-devel-ubuntu22.04). Here, the container builds on Ubuntu 22.04 with CUDA 12.1 pre-installed. - The rest of the file are optional data blobs or sections. In this example, the following blobs are used:
%post: the steps to download, configure and install needed custom software and libraries on the base image. In this example, the steps installgit, clone a repo, and install a package viamake%runscript: the entry point to the container with theapptainer runcommand. In this example, thedeviceQueryis executed once the container is run.- Other blobs may be present in the
deffile. See Definition files documentation for more details and examples.
And now, build this image and send it over to DAIC:
$ hostname #check this is your machine
$ apptainer build cuda_based_image.sif cuda_based.def # building may take ~ 2-5 min, depending on your internet
INFO: Starting build...
Getting image source signatures
Copying blob d5d706ce7b29 [=>------------------------------------] 29.2MiB / 702.5MiB
...
INFO: Adding runscript
INFO: Creating SIF file...
INFO: Build complete: cuda_based_image.sif
$
$ scp cuda_based_image.sif daic-login:/tudelft.net/staff-umbrella/...<YourDirectory>/apptainer # send to DAIC
On DAIC, check the image:
$ hostname # check you are on DAIC
login1.daic.tudelft.nl
$ sinteractive --cpus-per-task=2 --mem=1024 --gres=gpu --time=00:05:00 # request a gpu node
$ hostname # check you are on a compute node
insy13.daic.tudelft.nl
$ apptainer run --nv -C cuda_based_image.sif # --nv to use NVIDIA GPU and have CUDA support
/cuda-samples/Samples/1_Utilities/deviceQuery/deviceQuery Starting...
CUDA Device Query (Runtime API) version (CUDART static linking)
Detected 1 CUDA Capable device(s)
Device 0: "NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 Ti"
CUDA Driver Version / Runtime Version 12.1 / 12.1
CUDA Capability Major/Minor version number: 6.1
Total amount of global memory: 11172 MBytes (11714887680 bytes)
(028) Multiprocessors, (128) CUDA Cores/MP: 3584 CUDA Cores
GPU Max Clock rate: 1582 MHz (1.58 GHz)
Memory Clock rate: 5505 Mhz
Memory Bus Width: 352-bit
L2 Cache Size: 2883584 bytes
Maximum Texture Dimension Size (x,y,z) 1D=(131072), 2D=(131072, 65536), 3D=(16384, 16384, 16384)
Maximum Layered 1D Texture Size, (num) layers 1D=(32768), 2048 layers
Maximum Layered 2D Texture Size, (num) layers 2D=(32768, 32768), 2048 layers
Total amount of constant memory: 65536 bytes
Total amount of shared memory per block: 49152 bytes
Total shared memory per multiprocessor: 98304 bytes
Total number of registers available per block: 65536
Warp size: 32
Maximum number of threads per multiprocessor: 2048
Maximum number of threads per block: 1024
Max dimension size of a thread block (x,y,z): (1024, 1024, 64)
Max dimension size of a grid size (x,y,z): (2147483647, 65535, 65535)
Maximum memory pitch: 2147483647 bytes
Texture alignment: 512 bytes
Concurrent copy and kernel execution: Yes with 2 copy engine(s)
Run time limit on kernels: No
Integrated GPU sharing Host Memory: No
Support host page-locked memory mapping: Yes
Alignment requirement for Surfaces: Yes
Device has ECC support: Disabled
Device supports Unified Addressing (UVA): Yes
Device supports Managed Memory: Yes
Device supports Compute Preemption: Yes
Supports Cooperative Kernel Launch: Yes
Supports MultiDevice Co-op Kernel Launch: Yes
Device PCI Domain ID / Bus ID / location ID: 0 / 141 / 0
Compute Mode:
< Default (multiple host threads can use ::cudaSetDevice() with device simultaneously) >
deviceQuery, CUDA Driver = CUDART, CUDA Driver Version = 12.1, CUDA Runtime Version = 12.1, NumDevs = 1
Result = PASS
Tip: Enable GPU access
Always pass --nv to apptainer to run GPU-accelerated applications or libraries inside the container. Requirements:
- your host system must have NVIDIA GPU drivers installed and compatible with your Apptainer version, and
- the container must have the necessary dependencies and configurations to support GPU acceleration.
$ apptainer shell --nv -C cuda_based_image.sif
Note on reproducibility
Definition-file builds are the most reproducible approach. However, in cases of complex dependencies, you can first prototype interactively inwritable sandbox mode first. In such cases, take note of all installation commands used in the sandbox, so you can include them in a recipe file. See Apptainer Sandbox Directories for more details.Example: Extending existing images
During software development, it is common to incrementally build code and go through many iterations of debugging and testing.
To save time, you can base a new image on an existing one using the Bootstrap: localimage and From:<path/to/local/image> header.
This avoids re-installing the same dependencies with every iteration.
As an example, assume it is desirable to develop some code on the basis of the cuda_based.sif image created in the Example: CUDA-enabled container. Building from the original cuda_based.def file can take ~ 4 minutes. However, if the *.sif file is already available, building on top of it, via a dev_on_cuda_based.def file as below, takes ~ 2 minutes. This is already a time saving factor of 2.
# Header
Bootstrap: localimage
From: cuda_based.sif
# (Optional) Sections/ data blobs
%runscript
echo "Arguments received: $*"
exec echo "$@"
Now, build and test:
$ apptainer build dev_image.sif # build the image
INFO: Starting build...
INFO: Verifying bootstrap image cuda_based.sif
WARNING: integrity: signature not found for object group 1
WARNING: Bootstrap image could not be verified, but build will continue.
INFO: Adding runscript
INFO: Creating SIF file...
INFO: Build complete: dev_image.sif
$ apptainer run dev_image.sif "hello world" # check runscript of the new def file is executed
INFO: gocryptfs not found, will not be able to use gocryptfs
Arguments received: hello world
hello world
$ apptainer shell dev_image.sif # further look inside the image
Apptainer>
Apptainer> ls /cuda-samples/Samples/1_Utilities/deviceQuery/deviceQuery # commands installed in the original image are available
/cuda-samples/Samples/1_Utilities/deviceQuery/deviceQuery
Apptainer>
Apptainer> cat /.apptainer.d/bootstrap_history/Apptainer0 # The original def file is also preserved
bootstrap: docker
from: nvidia/cuda:12.1.1-devel-ubuntu22.04
%runscript
/cuda-samples/Samples/1_Utilities/deviceQuery/deviceQuery
%post
apt-get update # update system
apt-get install -y git # install git
git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/cuda-samples.git # clone target repository
cd cuda-samples
git fetch origin --tags && git checkout v12.1 # fetch certain repository version
cd Samples/1_Utilities/deviceQuery && make # install certain tool
As can be seen in this example, the new def file not only preserves the dependencies of the original image, but it also preserves a complete history of all build processes while giving flexible environment that can be customized as need arises.
Example: Deploying conda and pip in a container
There might be situations where you have a certain conda environment in your local machine that you need to set up in DAIC to commence your analysis. In such cases, deploying your conda environment in a container and sending this container to DAIC does the job for you.
As an example, let’s create a simple demo environment, environment.yml in our local machine,
name: apptainer
channels:
- conda-forge
- defaults
dependencies:
- python=3.9
- matplotlib
- pip
- pip:
- -r requirements.txt
And everything that should be installed with pip in requirement.txt file:
--extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu123
torch
annoy
Now, it is time to create the container definition file Apptainer.def. One option is to base the image on condaforge/miniforge, which is a minimal Ubuntu installation with conda preinstalled at /opt/conda:
Bootstrap: docker
From: condaforge/miniforge3:latest
%files
environment.yml /environment.yml
requirements.txt /requirements.txt
%post
# Update and install necessary packages
apt-get update && apt-get install -y tree time vim ncdu speedtest-cli build-essential
# Create a new Conda environment using the environment files.
mamba env create --quiet --file /environment.yml
# Clean up
apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
mamba clean --all -y
# Now add the script to activate the Conda environment
echo '. "/opt/conda/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"' >> $APPTAINER_ENVIRONMENT
echo 'conda activate apptainer' >> $APPTAINER_ENVIRONMENT
APPTAINER_ENVIRONMENT
The $APPTAINER_ENVIRONMENT variable in Apptainer refers to a special shell script that gets sourced when a container is run in shell mode. This is a key mechanism for setting up the environment for your container.
Here’s what’s happening in the code:
echo '. "/opt/conda/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"' >> $APPTAINER_ENVIRONMENT- This adds a command to source the Conda initialization script
- The script enables the
condacommand in your shell environment
echo 'conda activate apptainer' >> $APPTAINER_ENVIRONMENT- This adds a command to activate the “apptainer” Conda environment
- This ensures your container automatically starts with the right environment activated
When a user runs your container with apptainer shell my-container.sif, these commands will execute automatically, ensuring:
- The conda command is available
- The “apptainer” environment is activated
- All the Python packages specified in your
environment.ymlare available
This approach is much cleaner than requiring users to manually activate the environment every time they run the container. It makes your container more user-friendly and ensures consistent behavior.
This file is similar to the file in the Building images, with the addition of %files area. %files specifies the files in the host system (ie, your machine) that need to be copied to the container image, and optionally, where should they be available. In the previous example, the environment.yml file will be available in /opt/ in the container.
Now, time to build and check the image:
$ apptainer build demo-env-image.sif Apptainer.def
INFO: Starting build...
Getting image source signatures
...
INFO: Creating SIF file...
INFO: Build complete: Apptainer.sif
...
Let’s verify our container setup:
$ apptainer exec demo-env-image.sif which python
/opt/conda/envs/apptainer/bin/python
Perfect! This confirms that our container image built successfully and the Conda environment is automatically activated. The Python executable is correctly pointing to our custom environment path, indicating that all our dependencies should be available.
We are going to use the environment inside a container together with a Python script that we store outside the container.
Create the file analysis.py, which generate a plot:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.title('Sine Wave')
plt.savefig('sine_wave.png')
Now, we can run the analysis:
$ apptainer exec demo-env-image.sif python analysis.py
$ ls # check the image file was created
sine_wave.png
Warning
In the last example, the container read and wrote a file to the host system directly. This behavior is risky. You are strongly recommended to expose only the desired host directories to the container. See Exposing host directoriesExposing host directories
Depending on use case, it may be necessary for the container to read or write data from or to the host system. For example, to expose only files in a host directory called ProjectDataDir to the container image’s /mnt directory, add the --bind directive with appropriate <hostDir>:<containerDir> mapping to the commands you use to launch the container, in conjunction with the -C flag eg, shell or exec as below:
$ ls # check ProjectDataDir exists
$ ls ProjectDataDir # check contents of ProjectDataDir
raw_data.txt
$ apptainer shell -C --bind ProjectDataDir:/mnt ubuntu_latest.sif # Launch the container with ProjectDataDir bound
Apptainer> ls
Apptainer> ls /mnt # check the files are accessible inside the container
raw_data.txt
Apptainer> echo "Date: $(date)" >> raw_data.txt # edit the file
Apptainer> tail -n1 raw_data.txt # check the date was written to the file
Apptainer> exit # exit the container
$ tail -n1 ProjectDataDir/raw_data.txt # check the change persisted
If the desire is to expose this directory as read-only inside the container, the --mount directive should be used instead of --bind, with rodesignation as follows:
apptainer shell -C --mount type=bind,source=ProjectDataDir,destination=/mnt,ro ubuntu_latest.sif # Launch the container with ProjectDataDir bound
Apptainer> ls /mnt # check the files are accessible inside the container
raw_data.txt
Apptainer> echo "Date: $(date)" >> /mnt/raw_data.txt # attempt to edit fails
bash: tst: Read-only file system
Advanced: containers and (fake) native installation
It’s possible to use Apptainer to install and then use software as if it were installed natively in the host system. For example, if you are a bioinformatician, you may be using software like samtools or bcftools for many of your analyses, and it may be advantageous to call it directly. Let’s take this as an illustrative example:
- For hygiene, create the following file hierarchy: below a
softwaredirectory anexecdirectory to put the container images and other executables, and abindirectory to contain softlinks:
$ mkdir -p software/bin/ software/exec
- Create the image definition file (or pull from a repository, as appropriate) and build:
$ cd software/exec
$
$ cat bio-recipe.def
Bootstrap: docker
From: ubuntu:latest
%post
apt-get update # update system
apt-get install -y samtools bcftools # install software
apt-get clean # clean up
$ sudo apptainer build bio-container.sif bio-recipe.def
- Now, create the following wrapper script:
$ cat wrapper_bio-container.sh
#!/bin/bash
containerdir="$(dirname $(readlink -f ${BASH_SOURCE[0]}))"
cmd="$(basename $0)"
apptainer exec "${containerdir}/bio-container.sif" "$cmd" "$@"
$
$ chmod +x wrapper_bio-container.sh # make it executable
- Create the softlinks:
$ cd ../bin
$ ln -s ../exec/wrapper_bio-container.sh samtools
$ ln -s ../exec/wrapper_bio-container.sh bcftools
- Add the installation directory to your
$PATHvariable, and you will be able to call these tools
$ export PATH=$PATH:$PWD
$
$ bcftools -v
INFO: gocryptfs not found, will not be able to use gocryptfs
bcftools 1.13
Using htslib 1.13+ds
Copyright (C) 2021 Genome Research Ltd.
License Expat: The MIT/Expat license
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
$
$ samtools version
INFO: gocryptfs not found, will not be able to use gocryptfs
samtools 1.13
Using htslib 1.13+ds
Copyright (C) 2021 Genome Research Ltd.
Note
- At the end of the previous steps, you will get the following tree structure. Please be mindful of when and where commands were executed.
$ tree software/
software/
├── bin
│ ├── bcftools -> ../exec/wrapper.sh
│ └── samtools -> ../exec/wrapper.sh
└── exec
├── bio-container.sif
└── wrapper.sh
- To permanently reflect changes to your
$PATHvariable, you may wish to add the step:
echo export PATH=$PATH:$PWD >> ~/.bash_profile
3 - Installing and Using GurobiPy on DAIC
Installation
You can install GurobiPy using pip or conda in a virtual environment. Please refer to the Managing Environment manual for more information on using pip and conda.
# Using pip (in a virtual environment or with --user)
pip install gurobipy
# Or using Conda (in a virtual environment)
conda install gurobi::gurobi
Using GurobiPy
To use GurobiPy, you need to import the gurobipy module in your Python script. Here is an example script that creates a Gurobi model and solves it:
import gurobipy as gp
m = gp.Model()
m.optimize()
You can run the script using the following command:
$ sinteractive --ntasks=2 --mem=2G --time=00:05:00
$ python tst_gurobi.py
Restricted license - for non-production use only - expires 2026-11-23
Gurobi Optimizer version 12.0.1 build v12.0.1rc0 (linux64 - "Red Hat Enterprise Linux")
CPU model: AMD EPYC 7543 32-Core Processor, instruction set [SSE2|AVX|AVX2]
Thread count: 64 physical cores, 64 logical processors, using up to 32 threads
Optimize a model with 0 rows, 0 columns and 0 nonzeros
Model fingerprint: 0xf9715da1
Coefficient statistics:
Matrix range [0e+00, 0e+00]
Objective range [0e+00, 0e+00]
Bounds range [0e+00, 0e+00]
RHS range [0e+00, 0e+00]
Presolve time: 0.01s
Presolve: All rows and columns removed
Iteration Objective Primal Inf. Dual Inf. Time
0 0.0000000e+00 0.000000e+00 0.000000e+00 0s
Solved in 0 iterations and 0.01 seconds (0.00 work units)
Optimal objective 0.000000000e+00
Configuring the License
If needed, and since DAIC uses a remote license server, you can specify the license settings in your script:
import gurobipy as gp
connection_params = {
"TokenServer": "flexserv-x1.tudelft.nl",
"TSPort": 27099
}
with gp.Env(params=connection_params) as env:
with gp.Model(env=env) as model:
try:
populate_and_solve(model)
except:
# Add appropriate error handling here.
raise
4 - Running LLMs on DAIC
This guide shows you how to serve and use Large Language Models (LLMs) on DAIC using Ollama, a tool that lets you run models like Meta’s Llama models, Mistral models, or HuggingFace’s models for inference.
1. Clone the Template Repository
First, navigate to your project storage space. Then, clone the public REIT Ollama Serving repository. This ensures that all generated files, models, and containers are stored in the correct location, not in your home directory.
cd /tudelft.net/staff-umbrella/<your_project_name> # Replace with your actual project path
git clone https://gitlab.ewi.tudelft.nl/reit/reit-ollama-serving-template.git
tree reit-ollama-serving-template
Next, define and export the following environment variables:
| Variable | Value | Default |
|---|---|---|
PROJECT_DIR | Path where you like to store models/data for your project | |
CONTAINER_DIR | Directory where ollama container will be stored | ${PROJECT_DIR}/containers |
OLLAMA_DEBUG | Enable debug logging by setting to 1 | 0 |
Tip
PROJECT_DIRis the main directory for your project. To avoid$HOMEquota issues, it is recommended to use a path in yourbulkorumbrellastorage.CONTAINER_DIRis where the Ollama container image will be stored. The default is acontainerssubdirectory within yourPROJECT_DIR. If you want to change this location, make sure to update theCONTAINER_DIRvariable accordingly. Alternatively, if you have a pre-builtollama.sifimage, you can setOLLAMA_IMGto its path.- Setting
OLLAMA_DEBUGto1can help you troubleshoot issues by providing more detailed logs.
2. (Optional) Pull the Ollama Container
For simplicity, we will use the Ollama container image available on Docker Hub. You can pull it using Apptainer.
This step is optional, as the ollama-function.sh script will build the image automatically if it’s not found
in the ${CONTAINER_DIR} folder or as ${OLLAMA_IMG} file.
$ PROJECT_DIR=</path/to/your/project/in/umbrella/or/bulk/storage>
$ mkdir -p ${PROJECT_DIR}/containers
$ apptainer build ${PROJECT_DIR}/containers/ollama.sif docker://ollama/ollama
WARNING: 'nodev' mount option set on /tmp, it could be a source of failure during build process
INFO: Starting build...
Copying blob 6574d8471920 done |
Copying blob 13b7e930469f done |
Copying blob 97ca0261c313 done |
Copying blob e0fa0ad9f5bd done |
Copying config b9d03126ef done |
Writing manifest to image destination
2025/06/24 12:57:55 info unpack layer: sha256:13b7e930469f6d3575a320709035c6acf6f5485a76abcf03d1b92a64c09c2476
2025/06/24 12:57:56 info unpack layer: sha256:97ca0261c3138237b4262306382193974505ab6967eec51bbfeb7908fb12b034
2025/06/24 12:57:57 info unpack layer: sha256:e0fa0ad9f5bdc7d30b05be00c3663e4076d288995657ebe622a4c721031715b6
2025/06/24 12:57:57 info unpack layer: sha256:6574d84719207f59862dad06a34eec2b332afeccf4d51f5aae16de99fd72b8a7
INFO: Creating SIF file...
INFO: Build complete: /tudelft.net/staff-bulk/ewi/insy/PRLab/Staff/aeahmed/ollama_tutorial/containers/ollama.sif
Tip
For more on using Apptainer, see the Apptainer tutorial.3. Quick Interactive Test
- Start an interactive GPU session:
$ sinteractive --cpus-per-task=2 --mem=500 --time=00:15:00 --gres=gpu --partition=general
Note: interactive sessions are automatically terminated when they reach their time limit (1 hour)!
srun: job 11642659 queued and waiting for resources
srun: job 11642659 has been allocated resources
13:01:27 up 93 days, 11:16, 0 users, load average: 2,85, 2,60, 1,46
- Once you are allocated resources on a compute node, set your project directory, source the
ollama-function.shscript, and run the Ollama server (from the container):
export PROJECT_DIR=</path/to/your/project/in/umbrella/or/bulk/storage> # replace with your actual project path
source ollama-function.sh # Define the `ollama` function
ollama serve # The wrapper picks a free port and prints the server URL
Keep this terminal open to monitor logs and keep the Ollama server running.
Open a second terminal, login to DAIC, and interact with the server (e.g., from the login node). In the example below, we run the
codellamamodel
export PROJECT_DIR=</path/to/your/project/in/umbrella/or/bulk/storage> # Ensure this matches the server's PROJECT_DIR
source ollama-function.sh
ollama run codellama # Forwards the command to the running server
You can check the health of the server by running:
$ curl http://$(cat ${PROJECT_DIR}/ollama/host.txt):$(cat ${PROJECT_DIR}/ollama/port.txt)
Ollama is running
Ollama is running
- Interact with the model by typing your queries. For example, you can ask it to generate code or answer questions.
>>> who are you?
I am LLaMA, an AI assistant developed by Meta AI that can understand and respond to
human input in a conversational manner. I am trained on a massive dataset of text from
the internet and can answer questions or provide information on a wide range of topics.
>>>
- Stop the server with
Ctrl‑Cin the server terminal. Thehost.txtandport.txtfiles will be cleaned up automatically.
4. Production batch jobs
The template already provides ready‐to‐run Slurm scripts. For convenience a single helper, start-serve-client.sh ,
submits the server and client jobs in the right order and passes your PROJECT_DIR into both jobs.
To submit your jobs:
bash start-serve-client.sh \
-p </path/to/your/project/in/umbrella/or/bulk/storage> # Specify your project path. Defaults to `$PWD` if omitted.
What happens:
- Sets
PROJECT_DIRto the path you pass (or defaults to$PWDifPROJECT_DIRomitted), - Submits
ollama-server.sbatchrequesting GPU resources for serving your model - Submits
ollama-client.sbatchwith--dependency=after:<server‑id>so it starts as soon as the server begins running.
To check progress of these jobs:
squeue -j <server‑job-id>,<client‑job-id>
Once the jobs have run, the typical logs are:
log-ollama-server-<server-job-id>.out: showing the server has started and where it is running.log-ollama-client-<client-job-id>.log: Showing example workflow of pulling a model (deepseek-r1:7b), sending a prompt to the model and printing the response.
Client jobs
- As long as the server job is running you can submit additional client jobs that point to the same
PROJECT_DIR - You can inspect the
ollama-client.sbatchfile for examples of how to interact with the server (from the command line or within scripts)
5. Best Practices
While you can run Ollama manually, the wrapper scripts provide several conveniences:
- Always serve on a GPU node. The wrapper prints an error if you try to serve from a login node.
- Client jobs don’t need
--nv. The wrapper omits it automatically when no GPU is detected, eliminating noisy warnings. - Model cache is project‑scoped. All model blobs land in
$PROJECT_DIR/ollama/models, so they don’t consume$HOMEquota. - Image builds use
/tmp. The wrapper builds via a local cache to avoid premission errors. - Automatic cleanup. The wrapper cleans up
host.txtandport.txtfiles after the server stops, so you can tell if you have a server up and running.
6. Troubleshooting
| Symptom | Fix |
|---|---|
host.txt / port.txt not found | Start the server first: ollama serve (interactive) or submit ollama-server.sbatch. |
Could not find any nv files on this host! | Safe to ignore; client ran on CPU. |
Build fails with operation not permitted | Ensure the wrapper’s /tmp build cache patch is in place, or add --disable-cache. |
## Acknowledgment
Inspirtation for this tutorial comes from the Stanford ollama_helper repository.
The DAIC template adapts many of the same ideas to TU Delft’s Slurm environment.